
TOPIC: Introduction and Types of Generators
ELECTROMAGNETIC
INDUCTION
When there
is a
change in
the number
of
magnetic
lines of
force
linked
with a
coil, an
induced
emf is
developed
in the
coil. The
phenomenon
is known
as
electromagnetic
induction.
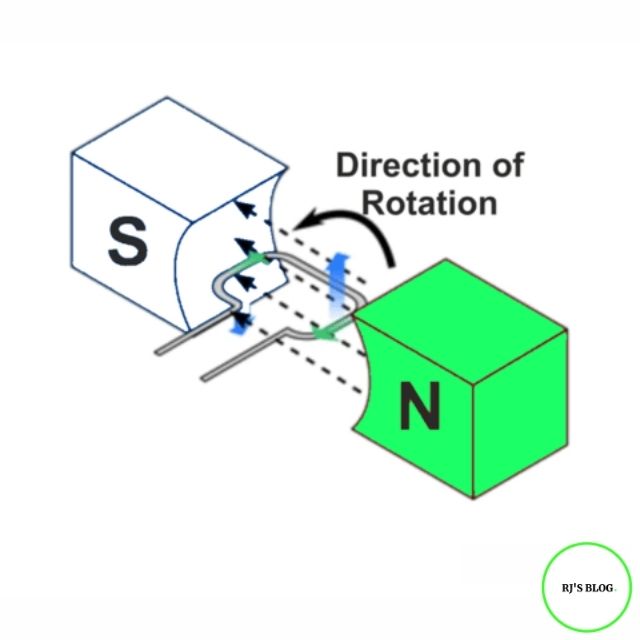 Figure: Generator
Figure: Generator
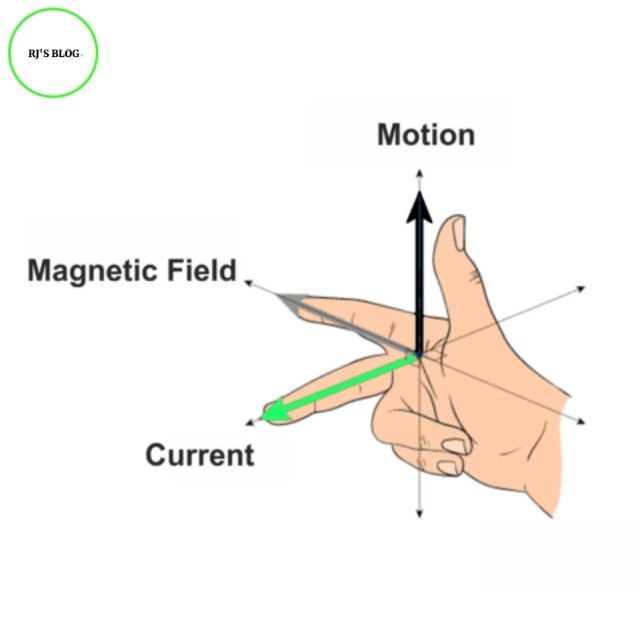 Figure: Demonstration of Fleming's Right Hand Rule
Figure: Demonstration of Fleming's Right Hand Rule
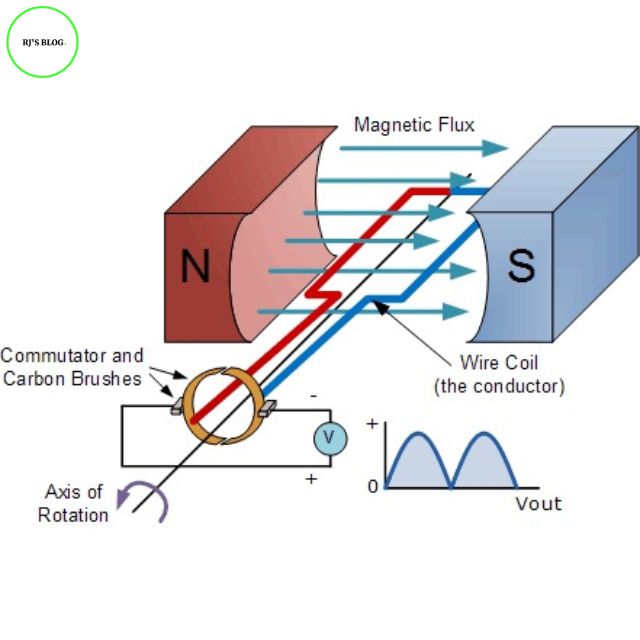 Figure: AC Generator
Figure: AC Generator
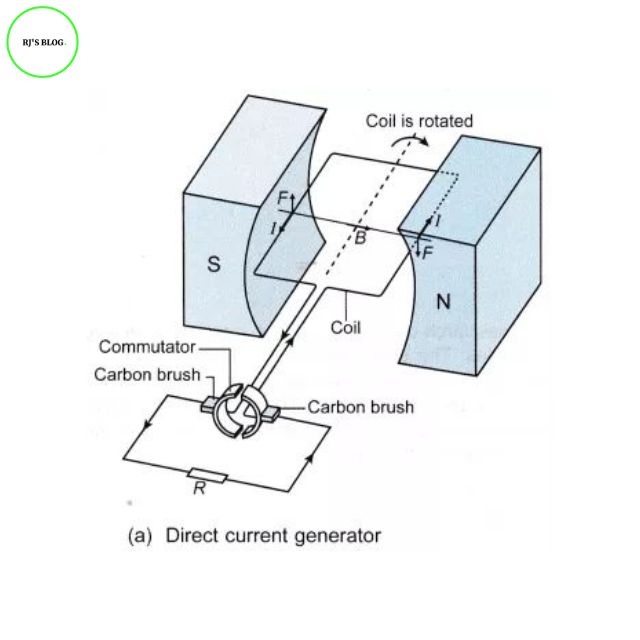 Figure: DC Generator
Figure: DC Generator
| AC | DC |
|---|---|
| 1. Current changes its direction periodically. | 1. Current flows in one direction only. |
| 2. The frequency of the AC is desirable/ can be set at any level. | 2. The frequency of DC is zero DC has no frequency. |
| 3. The voltage of AC can be stepped up or stepped down with the help of a transformer. | 3. The voltage of Dc cannot be changed. |
| AC Generator | DC Generator |
|---|---|
| 1. AC generator produces AC in which current changes its direction periodically. | 1. DC generator produces direct current in which flows in one direction only. |
| 2. In AC generator two slip rings are used. | 2. In DC generator only one slip ring is used. |
| 3. In AC generator the two slip rings are in contact with the two brushes constantly and separately. | 3. In DC generator the two half rings are in contact with the two brushes alternately in the right time. |
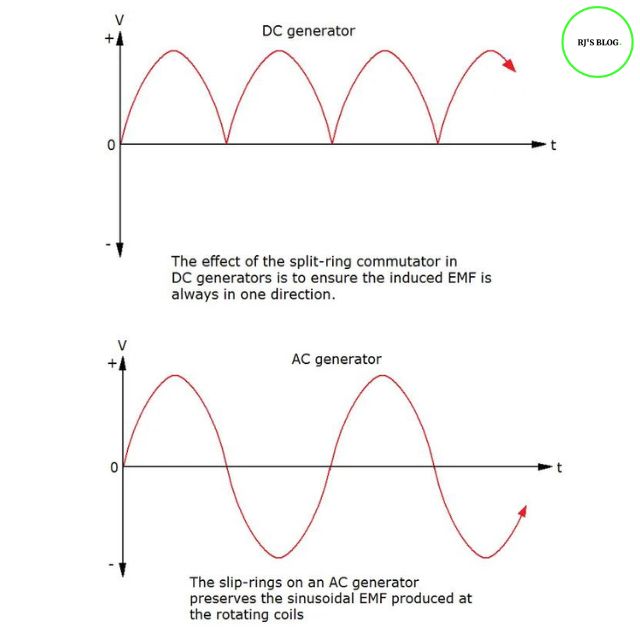 Figure: Nature of emf
Figure: Nature of emf
Induction for deduction, with a view to construction
- Auguste Comte