

TOPIC: Diamond, Graphite and Hydrocarbons
As a continuation of the previous blog on Carbon and its
Compounds, let us discuss some more important terms and topics.
DIAMOND:
Hardness of Diamond
In diamond, each carbon atom lies at the center of a regular
tetrahedron and is covalently bonded with four carbon atoms
located at its four corners. The tightly bonded three-dimensional
tetrahedral arrangement of carbon atoms produces a rigid network
and makes diamond the hardest substance.
Structure of Diamond
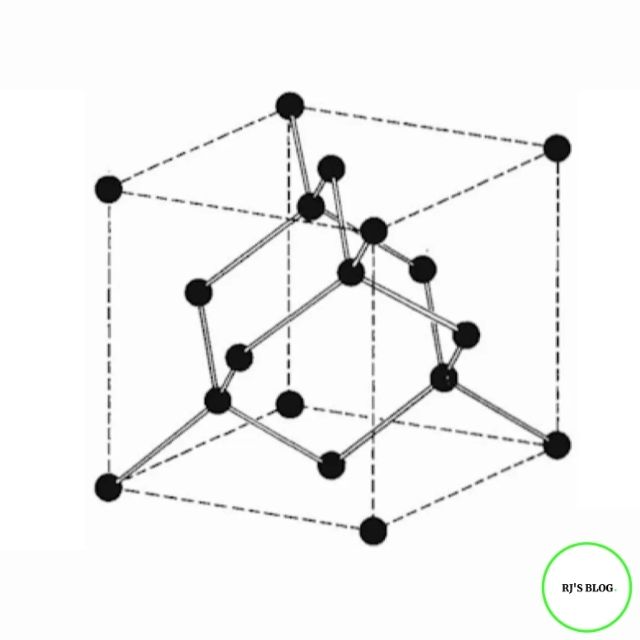 Figure: Structure of Diamond
Figure: Structure of Diamond
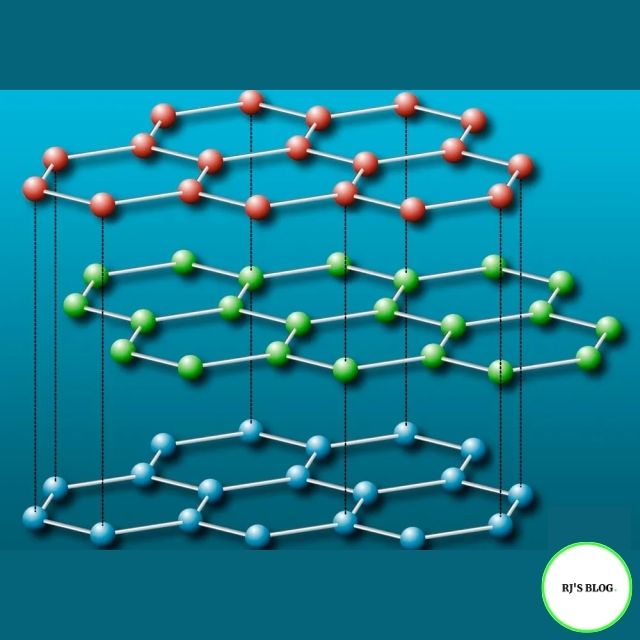 Figure: Structure of Graphite
Figure: Structure of Graphite
More about Saturated
Hydrocarbons
Alkanes
Open chain hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are linked by
single bonds only are called Alkanes. The general formula of
alkane is: CnH2n+2, where n = 1, 2, 3, ...
For example: C2H6 - Ethane.
Alkyl:
A group of atoms obtained by removing one hydrogen
atom from an Alkane are called Alkyl. The general formula of
alkyl is: CnH2n+1, where n = 1, 2, 3,
...
For example: C2H5 - Ethyl.
Cycloalkanes
Close chain hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are linked by
single bones only, also called cyclix are called Cycloalkanes.
Its general formula is CnH2n.
For example: C3H6 - Cyclopropane.
We define organic chemistry as the chemistry of carbon compounds
- August Kekule
More about Unsaturated
Hydrocarbons
Alkenes
The unsaturated hydrocarbons which contain double bonds are
called Alkenes. Its general formula is
CnH2n.
For example: C4H8 - Butene.
Alkynes
Open chain hydrocarbons containing carbon-carbon triple bond are
called Alkynes. Its general formula is
CnH2n-2.
For example: C4H6 - Butyne.